Moderna/Pfizer Shots Force Body to Produce Unintended Enzyme that Doubles mRNA Tail Length, Extends Spike Protein Production: Journal 'Nature'
COVID shots don't just deliver mRNA—they reprogram your immune cells to keep it alive longer, rewrite it, and produce more spike than you were told.
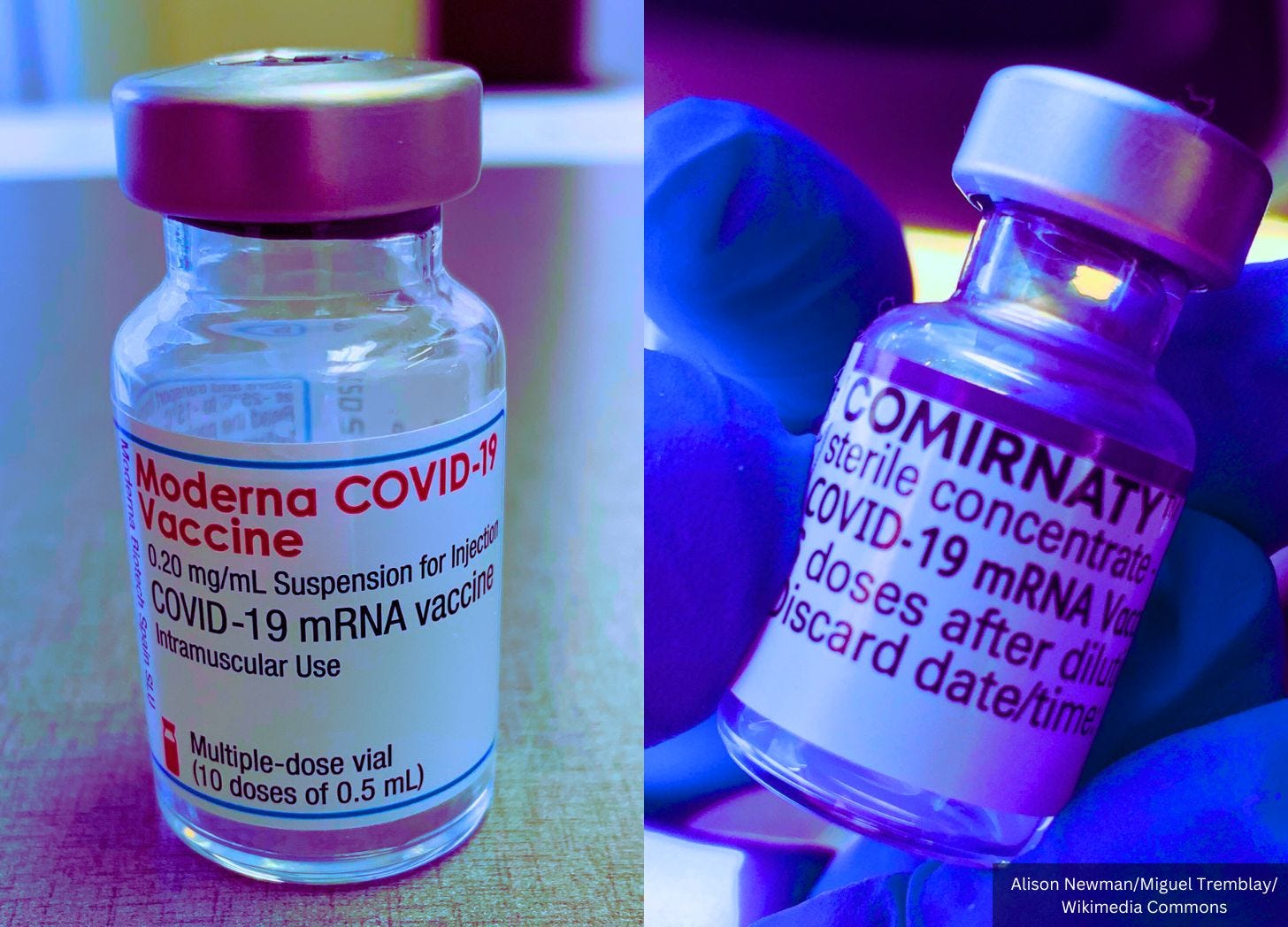
A bombshell new study published last month in Nature confirms what vaccine manufacturers never disclosed: Both Moderna and Pfizer’s COVID-19 mRNA injections induce the body to produce an enzyme that rewrites the vaccine’s genetic message—prolonging spike protein production inside human cells.
Health authorities told us the spike protein only stays in the body “up to a few weeks,” but this website has reported on studies showing COVID shots force the body to produce spike protein for 187 days, 245 days, and even 709 days.
Moderna’s own scientists have admitted their mRNA vaccines pose “unacceptable toxicity” risks that present “challenges,” even going so far as to publish a paper in Nature Reviews Drug Discovery in January 2024 outlining strategies to “reduce the risks of mRNA drug and vaccine toxicity.”
Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood
The new Polish study, titled “Re-adenylation by TENT5A enhances efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines” (Krawczyk et al., 2025), reveals that after the mRNA vaccines are injected, immune cells called macrophages respond by producing a non-canonical poly(A) polymerase enzyme called TENT5A, meaning your body makes an enzyme it doesn’t usually produce—because the vaccine tells it to.
You can download the study below:
TENT5A’s role is to extend the poly(A) tail of the mRNA, meaning it adds a long string of A’s (adenine nucleotides) to the end of the vaccine's genetic code, making it more stable and longer-lived inside the cell.
This makes the mRNA survive longer than it naturally would and continue producing spike protein over an extended period.
“In vivo, TENT5A is expressed in immune cells that take up mRNA vaccine,” write the authors, adding that its absence “reduces specific immunoglobulin production.”
But TENT5A doesn’t just help the immune system.
It acts directly on the vaccine mRNA itself, modifying it after injection to increase its lifespan, meaning the body unintentionally helps the vaccine last longer than it was originally designed to.
In some cells, the study found that the poly(A) tail of Moderna’s mRNA increased from 100 to as much as 200 nucleotides, meaning the molecule that controls how long the mRNA stays alive and active was doubled in length.
What Does That Mean?
It means the body is induced to generate an enzyme that rewrites the COVID shot after injection, stabilizing it and amplifying spike production beyond what was disclosed in regulatory filings.
Your body could be exposed to more spike protein, for longer, than anyone was told during the shot’s rollout, confirming other studies showing spike stays in the body potentially for more than 700 days.
Not Just Moderna
While Moderna’s vaccine (mRNA-1273) showed the most dramatic re-adenylation, Pfizer’s shot (BNT162b2) also undergoes the same process—just to a lesser degree.
So the problem isn’t limited to one manufacturer.
“The extent of re-adenylation varies: the BioNTech–Pfizer BNT162b2 vaccine shows less potent re-adenylation than mRNA-1273,” the study states, attributing this to Pfizer’s mRNA being less associated with the cell’s endoplasmic reticulum, meaning Pfizer’s mRNA spends less time near the cell’s protein-making machinery, so it doesn’t get modified as aggressively.
In other words: Both vaccines trigger this effect, but Moderna’s formulation causes more sustained and aggressive modification of the vaccine mRNA by the body itself, meaning Moderna’s spike production is likely even longer-lasting.
Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood
The Mechanism: Hijacking Your Immune Cells
Here’s how it works, according to the study:
Once the lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-encapsulated mRNA is injected, it is taken up by immune cells—especially macrophages, meaning the same white blood cells responsible for cleaning up infection and dead tissue.
The presence of foreign mRNA and spike production causes inflammation and cellular stress, especially at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), meaning the part of the cell where proteins are built gets overwhelmed.
In response, these immune cells activate gene expression programs, including the upregulation of TENT5A, meaning they switch on new genes that weren’t active before, including the one that makes the TENT5A enzyme.
TENT5A then attaches to the vaccine mRNA, recognizes it as an ER-targeted message, and extends its poly(A) tail, meaning it modifies the mRNA to make it last longer in the cell.
The result? More spike protein, over a longer period of time, in precisely the immune cells responsible for presenting antigens, meaning the body keeps producing spike from a shot it thought was temporary.
“The extent of re-adenylation varies… This highlights the crucial role of spatial accessibility to ER-resident TENT5A in determining re-adenylation efficiency,” the authors explain, meaning how close the vaccine mRNA gets to the ER decides how much it gets modified and prolonged.
A Hidden Layer of Genetic Amplification
None of this was disclosed to the public, physicians, or patients.
The effect was not part of the original safety trials or regulatory submissions.
Yet the implications are profound: The vaccine mRNA is not static—it is modified by your own cells after injection in ways that can increase both the duration and intensity of spike protein production, meaning your body isn’t just following instructions—it’s changing them to make the shot stronger and longer-lasting.
“We show that the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated TENT5A poly(A) polymerase stabilizes IVT mRNAs… Our findings reveal a principle for enhancing the efficacy of therapeutic mRNAs,” the study concludes.
“Enhancing efficacy” here means enhancing persistence, meaning keeping synthetic mRNA active longer so it produces more protein than originally intended.
What About Novavax?
Interestingly, the same effect was not seen with Novavax, a protein-based shot that does not use mRNA, meaning this problem appears to be unique to the mRNA platform.
That strongly suggests this modification is a hidden feature of lipid nanoparticle-delivered mRNA shots, not a general property of all vaccines.
Still Think the mRNA Just Disappears?
Health authorities long claimed the mRNA in these shots degrades quickly.
But the new Nature study shows the opposite: In some cases, it’s not just persisting—it’s being extended and stabilized by the immune system itself, meaning the body keeps the vaccine message alive when it was supposed to shut it down.
In short: Moderna and Pfizer’s mRNA COVID shots reprogram your immune cells to make more of the very code that your body was told it would briefly read and discard, meaning the shots linger, alter themselves, and amplify their effect—all without your knowledge or consent.
This wasn’t just a case of mRNA lasting longer than expected—it’s a case of your own body being coerced into rewriting, prolonging, and amplifying a synthetic genetic code it was never supposed to keep.
Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood









It seems that so many new studies claim what anti-vaxxers feared. The shots never end. It’s not as though it helps raise immunity. But rather the spike protein continues wreaking havoc. Patients should get detoxed and go to a functional regenerative alternative medicine practitioner.
All "vaccines" are bioweapons. At best, they mask one symptom yet cause many more. Lifelong dependency on their drugs as a result. See the end of this Substack for the CDC vaccine excipient list. Foreign DNA, aluminum, mercury and more. Oh my! Run for the hills. https://substack.com/@mellowkat/note/p-163506459?utm_source=notes-share-action&r=gecv9