Moderna Patent Says Vitamin C May Block Spike Protein Production in COVID-19 Jab
Potential good news for those who regret taking the mRNA COVID shot.
Moderna Inc.’s patent for its mRNA COVID-19 injection’s lipid nanoparticle (US11622972B2) reveals that vitamin C (ascorbic acid) may significantly hinder spike protein production by creating impurities known as “adduct impurities.”
Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood / Facebook @realjonfleetwood
These impurities form when certain molecules, such as lipids, attach to the mRNA within the vaccine’s lipid nanoparticle (LNP) system, potentially blocking the mRNA’s ability to produce the spike protein, which the company says is necessary for triggering an immune response.
The patent describes these impurities as follows:
The term “adduct” or “adduct impurity” refers to the covalent addition of a lipid or other entity (e.g., hydrophobic entity) or polymer chain to a polynucleotide, such as mRNA. An “ionizable lipid-polynucleotide adduct impurity” (also referred to as “impurity group” or “IG”) is a type of adduct that comprises the covalent modification of a polynucleotide (e.g., in a LNP) with an ionizable lipid or a derivative thereof.
When these impurities attach to the mRNA, they can disrupt its ability to be translated into proteins, which could stop the production of the spike protein.
According to the patent, “The presence of adduct impurities can lead to low translation competency of the polynucleotide of the adduct impurity. For instance, in the context of mRNA an adduct includes covalent modification of the mRNA in such a way as to prevent translation of the mRNA.”
This means that these impurities can block the mRNA from producing the spike protein.

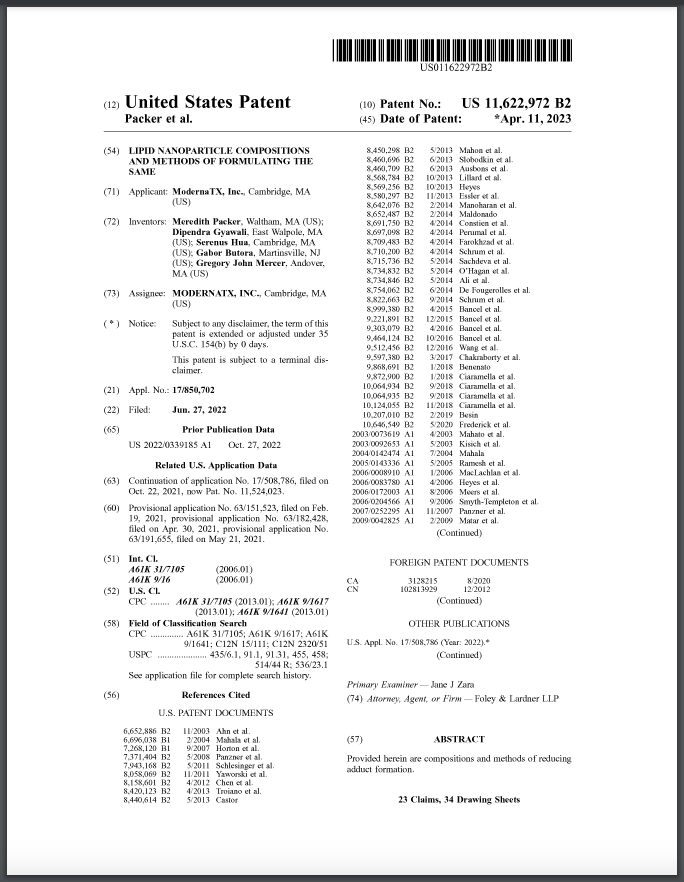
Figure 14 in the patent provides perhaps the strongest evidence, showing that ascorbic acid (vitamin C) leads to the highest levels of these impurities compared to other agents tested.
The patent notes:
FIG. 14 is a graph showing percentage of IG detected in LNP compositions comprising mRNA and Compound III or comprising mRNA, Compound III, and 1 mM of select anti-oxidants—e.g., ascorbic acid, L-cysteine, BHA, methionine, lipoic acid, homo cysteine, DDT, DTE, cystamine, DTT, glutathione, N-acetyl cysteine, sodium borohydrate, sodium thiosulfate, TCEP, or sodium thioglycolate, or potassium metabisulfite.
Vitamin C, listed as ascorbic acid, shows the highest impurity formation, suggesting it may be particularly disruptive to the vaccine’s intended function.

While antioxidants like vitamin C are generally used to stabilize molecules, in this case, the presence of ascorbic acid may lead to more impurities rather than fewer, potentially impairing the mRNA’s capacity to produce the spike protein.
The other substances listed in the graph (Figure 14) from the patent, which contribute to impurity formation in the vaccine’s lipid nanoparticles, include:
L-cysteine
BHA (Butylated Hydroxyanisole)
Methionine
Lipoic acid
Homo cysteine
DDT (Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane)
DTE (Dithioerythritol)
Cystamine
DTT (Dithiothreitol)
Glutathione
N-acetyl cysteine
Sodium borohydrate
Sodium thiosulfate
TCEP (Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine)
Sodium thioglycolate
Potassium metabisulfite
These antioxidants and reducing agents were tested to see how much impurity they would form, with vitamin C (ascorbic acid) showing the highest level.
Moderna’s patent suggests that vitamin C could interfere with the mRNA COVID-19 shot by generating impurities that block spike protein production.
Dr. Richard Bartlett Weighs In
Dr. Richard Bartlett, an ER director, Meritorious Service Award recipient from Texas Health and Human Services, and former advisor to then-Governor Rick Perry’s Health Disparities Task Force, describes the frequent calls he receives from patients struggling with adverse effects believed to be linked to spike protein persistence.
“I frequently get calls from across the state asking what a patient can do to detoxify from the spike protein because they are having adverse symptoms,” he told this website on Friday.
Dr. Bartlett points to a significant discovery in the Moderna patent, which offers insight into a potential approach for mitigating spike protein production using a widely available nutrient.
“The Moderna patent leaves evidence of a treatment strategy using vitamin C to disrupt spike protein production,” he said. “This is good news.”
The Texas physician underscores the importance of this finding, reminding us that:
“The spike protein is what causes the pathology of all disease symptoms of COVID.”
mRNA Jab Risks
mRNA jabs are associated with many problems that lead to negative health outcomes, including ingredients like pseudouridine being linked to cancer growth, frameshifting linked to immune system disorders, DNA contamination, and spike protein toxicity.
A January study published by Moderna scientists in Nature Reviews Drug Discovery confirms there are toxicity risks associated with COVID shots that use mRNA-based platforms.
The study states that “avoiding unacceptable toxicity with mRNA drugs and vaccines presents challenges” and that “[l]ipid nanoparticle structural components, production methods, route of administration and proteins produced from complexed mRNAs all present toxicity concerns.”
This website has reported how COVID jab spike protein is associated with prolonged presence in human tissue (up to 245 days), immune disorders causing severe inflammation, and enhanced cancer cell survival during chemotherapy.
For those who regret taking the mRNA COVID-19 shot, this patent offers some hope: if vitamin C can interfere with spike protein production, it may help reduce the potential negative health effects associated with the shot, including issues like spike protein toxicity and immune system disorders.
Editor’s Note: This article builds on the pioneering work and findings of Dr. Ana Maria Mihalcea, who, in a recent interview with Children’s Health Defense, reported discovering “blinking lights” and “self-assembling nanotechnology” in the blood of individuals who received COVID-19 shots, which she describes as potentially forming “microchips” capable of emitting signals. You can watch Dr. Mihalcea’s presentation on vitamin C and the COVID jab here.
Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood / Facebook @realjonfleetwood
Moderna Scientists Admit 'Risks of mRNA Drug and Vaccine Toxicity': Journal 'Nature'
A study published Tuesday in Nature Reviews Drug Discovery confirms there are toxicity risks associated with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines like those from Pfizer Inc. and Moderna Inc.
FDA Greenlights New Bill Gates-Funded ARCT-2304 Self-Replicating samRNA 'Pandemic' H5N1 Bird Flu Jab
Arcturus Therapeutics, a company specializing in mRNA-based pharmaceuticals, quietly announced Monday that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted approval for its Investigational New Drug (IND) application for ARCT-2304, a self-amplifying mRNA (sa-mRNA) injection targeting the H5N1 avian influenza “bird flu” virus.
COVID Jab Spike Protein Linked to 'Life-Threatening' Immune Disorder Causing Severe Inflammation: Journal 'Infectious Disorders - Drug Targets'
A Monday publication in the peer-reviewed medical journal Infectious Disorders - Drug Targets confirms the link between the spike protein that the COVID-19 jab forces the body to produce and the immune disorder Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS).
COVID-19 Jab mRNA and Spike Protein Stay in Human Tissue Longer Than Expected: Journal 'British Pharmacological Society'
A new review article published Wednesday in the journal British Pharmacological Society confirms COVID-19 jab mRNA can last up to a month in the body, and spike proteins can persist over six months, potentially causing cardiotoxicity and immune response issues, with ingredient N1-methyl-pseudouridine (m1Ψ) contributing to these risks.
COVID Jab Spike Protein Remains in Body 'Up to 245 Days'—Not a 'Few Weeks' as Health Authorities Claimed: Journal 'MedRxiv'
A March publication in the peer-reviewed medical journal MedRxiv confirms that the spike protein produced by cells after mRNA COVID-19 injection remains in the body for “up to 245 days,” contradicting claims from mainstream health authorities.
COVID Spike Protein—Present in Pfizer, Moderna mRNA Jabs—Helps Cancer Cells Survive Chemotherapy: Brown University Study Preprint in 'BioRxiv'
Brown University researchers posted a preprint study last month in BioRxiv, an open-access preprint repository for the biological sciences, confirming that the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interferes with the effectiveness of chemotherapy treatment for cancer.
'Blinking Lights' and 'Self-Assembling Nanotech' Found in COVID-19-Jabbed: Dr. Ana Mihalcea (Video)
In a startling new interview with Children’s Health Defense (CHD), Dr. Ana Maria Mihalcea, MD, PhD, claims to have identified “blinking lights” in the blood of individuals who have received a COVID-19 shot.










This is excellent news. There are now three known ways to combat the spike protein. First is to try to degrade the protein with nattokinase, bromelain and curcumin as per the McCollough protocol. Second is to try to stop the spike proteins from attaching to cellular receptors with nicotine or ivermectin. Third is to try to stop or slow the protein from being produced in the first place with vitamin C.
JON…Checkout out Dr. Ana Mihalcea substack and her protocol for the bio weapons injections that is EDTA and high doseage of vitamin C . I’ve been on this for six months. She’s amazing and very knowledgeable about clots, etc.