Pfizer COVID Jab Linked to 'State-of-the-Art Technology Within a U.S. Weapon System': National Archives Redaction Code Hides Information in U.S. Military, FDA Documents
Redacted Pfizer COVID vaccine documents suggest a potential link to U.S. weapon system technology, raising concerns about hidden military implications in public health data.
Summary:
Pfizer’s COVID shot safety data includes redacted sections using a U.S. National Archives code linked to weapon system technology.
The FDA initially sought to delay the release of this data for 75 years but was ordered by a federal judge to expedite the process.
The redaction code appears in documents from Pfizer, the FDA, and the U.S. military, suggesting a possible dual-use of technology.
Historical parallels are drawn to the U.S. bioweapons programs, raising concerns about the overlap between public health and national security.
The use of this code fuels speculation about the true nature of the technology involved and the transparency of the vaccine’s development.
These redactions prompt questions about potential conflicts of interest and the balancing of public health with defense strategies.
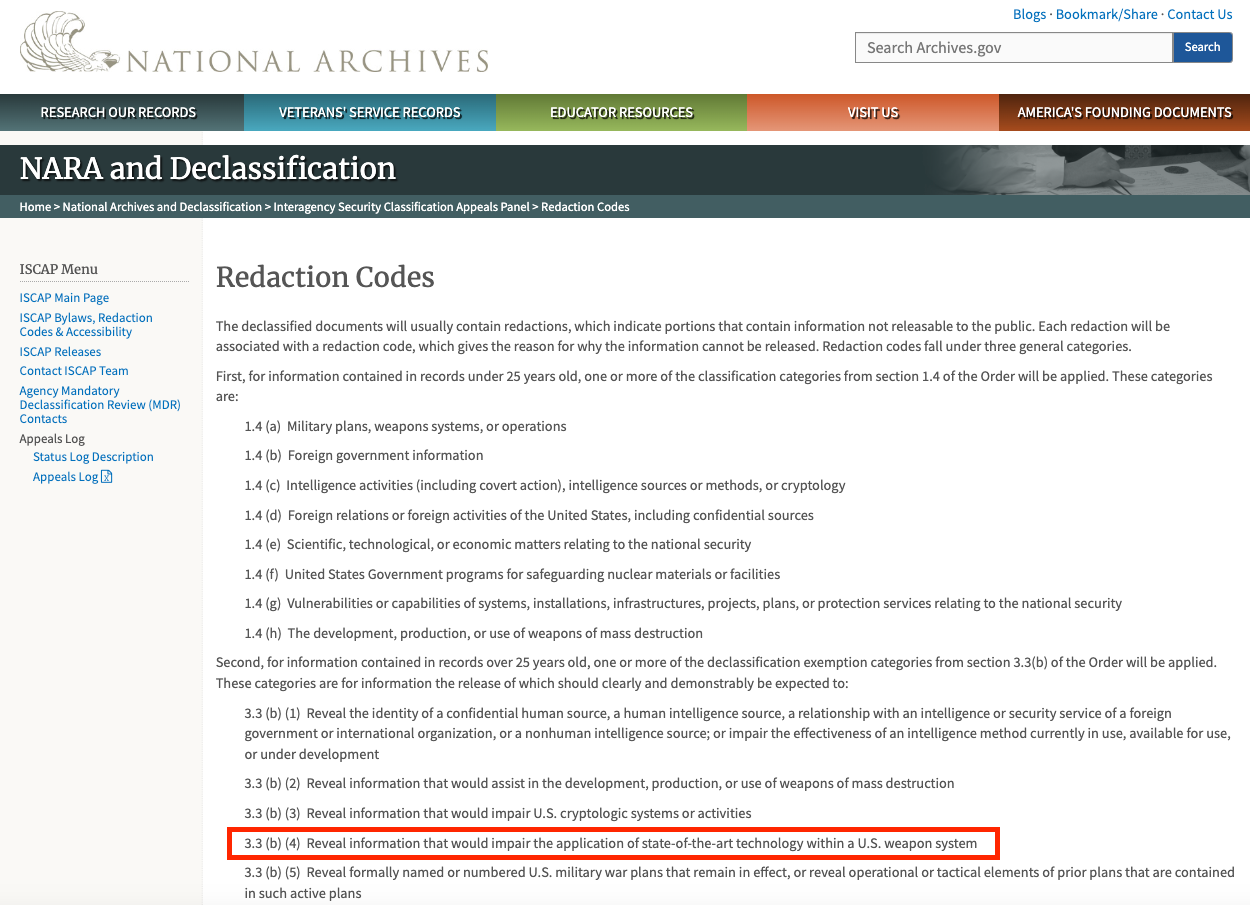
Blacked-out sections of Pfizer Inc.’s mRNA COVID-19 jab safety data made public by Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) request display a U.S. National Archives code that indicates the information hidden by the redactions would “[r]eveal information that would impair the application of state-of-the-art technology within a U.S. weapon system.”
Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood / Facebook @realjonfleetwood
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) wanted 75 years to release the data, but a federal judge in Texas in January 2022 ordered the agency to turn over 55,000 pages of data per month.
The order was made by Trump-appointed U.S. District Judge Mark Pittman in Fort Worth, who concluded the FOIA request was “of paramount public importance.”
Lawyer Aaron Siri of Siri & Glimstad, who represented plaintiffs Public Health and Medical Professionals for Transparency (PHMPT), said the decision “came down on the side of transparency and accountability.”
The code appears in Pfizer’s documents as well as documents from the FDA and U.S. military.
‘U.S. Weapon System’ Redaction Code in Pfizer Documents
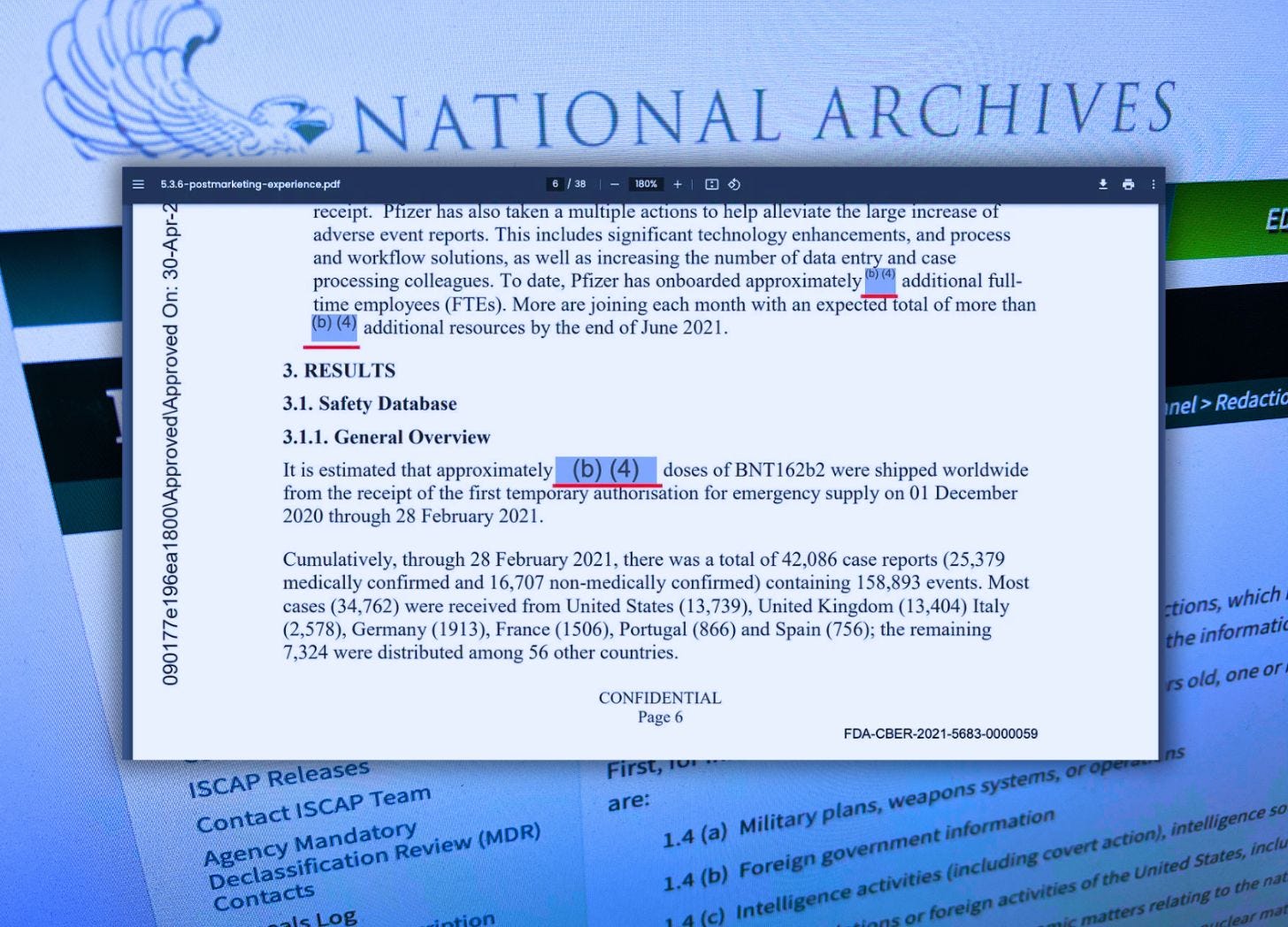
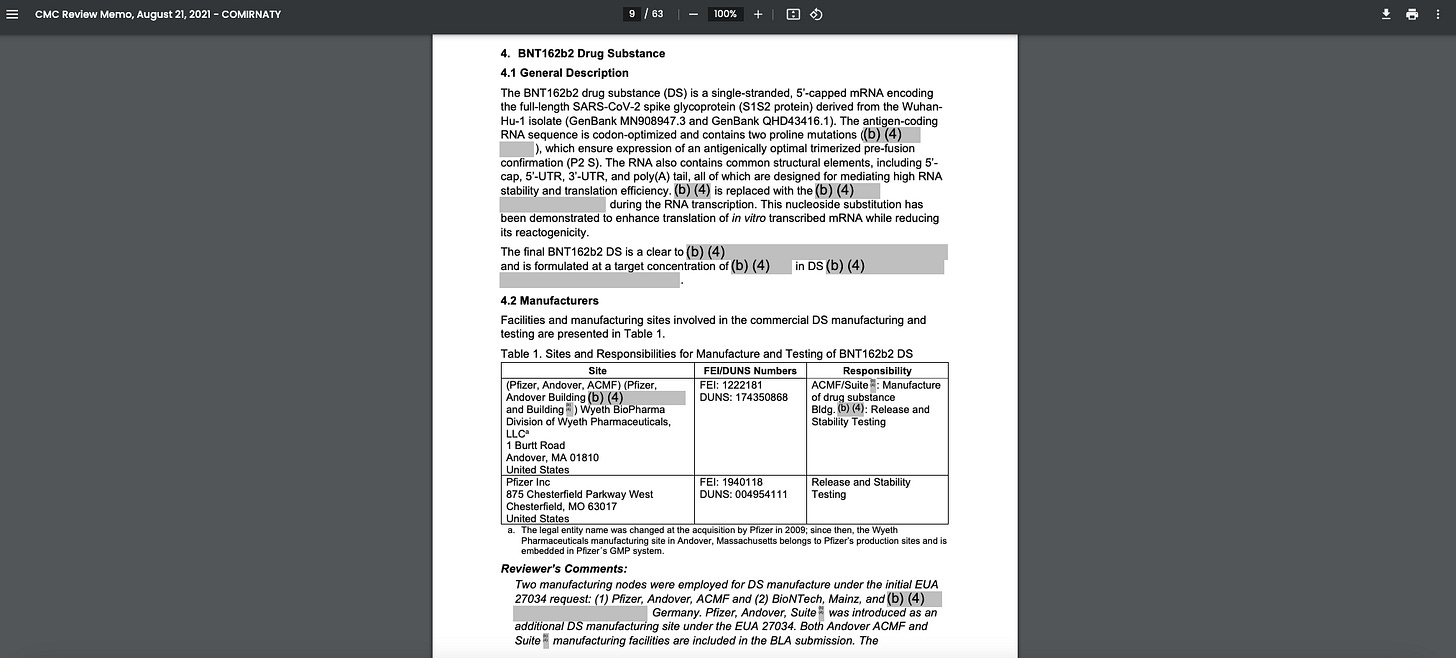
One of these documents that PHMPT makes available on its website is titled “5.3.6 CUMULATIVE ANALYSIS OF POST-AUTHORIZATION ADVERSE EVENT REPORTS OF PF-07302048 (BNT162B2) RECEIVED THROUGH 28-FEB-2021.”
This Pfizer data reveals more than 1,200 diseases are linked to the company’s coronavirus jab.
In two sections, titled “METHODOLOGY” and “RESULTS,” portions of the data are covered by black boxes displaying the symbols and numbers “(b) (4).”
According to the National Archives, the (b) (4) code represents a “declassification exemption categor[y]” for information the release of which is expected to “[r]eveal information that would impair the application of state-of-the-art technology within a U.S. weapon system.”

Military Documents
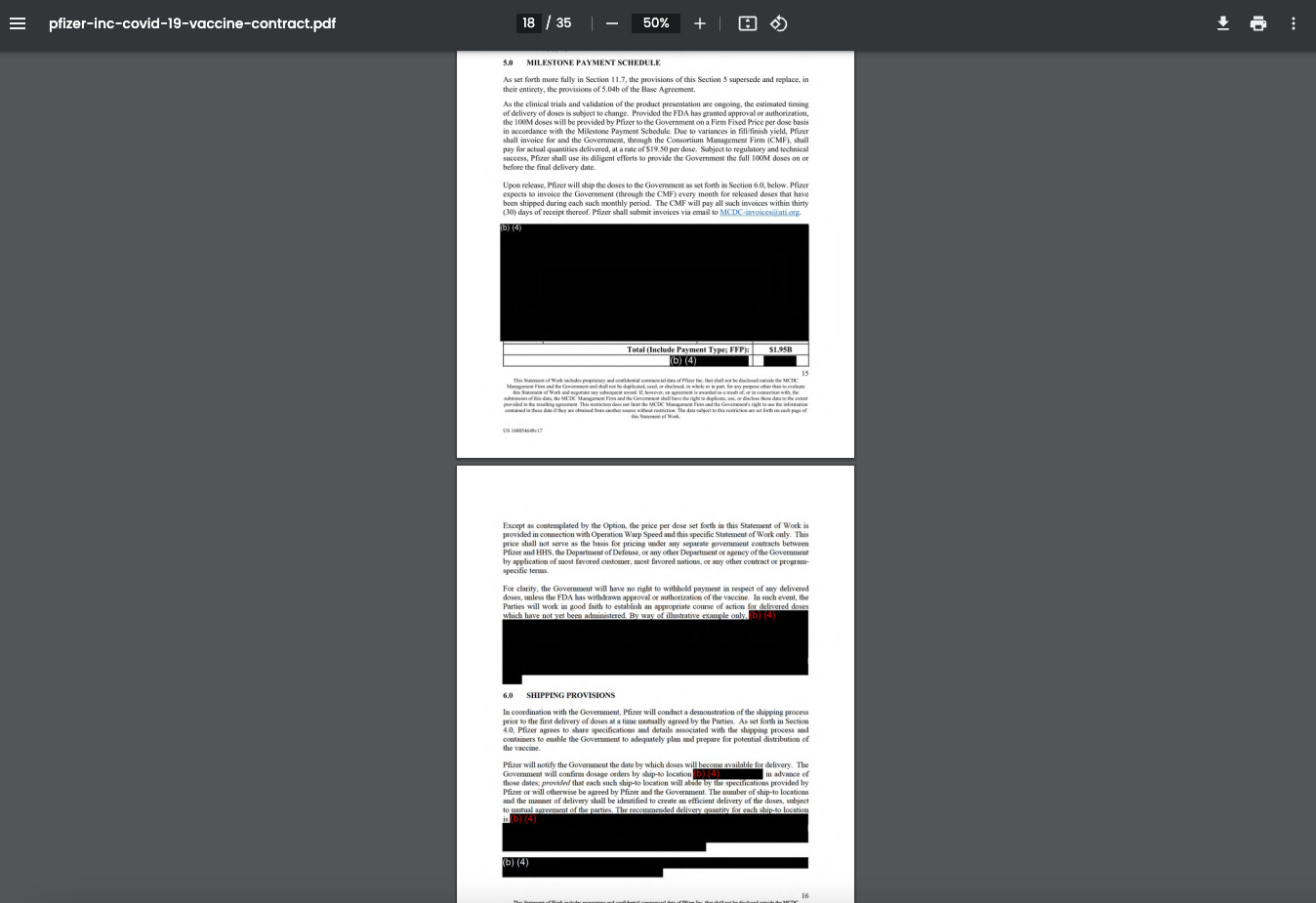
The code also appears on Department of Defense (DoD) documents related to a technical direction from the U.S. military regarding a request for prototype proposals focused on COVID-19 vaccine manufacturing.
On July 21, 2020, the U.S. Army Contracting Command in New Jersey issued a Technical Direction Letter related to the Medical CRBN Defense Consortium’s Request for Prototype Proposals (RPP) 20-11, which focuses on large-scale manufacturing of COVID-19 vaccines.
The Medical CRBN Defense Consortium was formed to support DoD’s efforts in developing medical countermeasures against CBRN (Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear) threats.
The letter indicates Pfizer had been selected as the awardee for the project, with funding not exceeding $1,950,097,500.
Notably, the document includes large sections blacked out with the (b) (4) code.

Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood / Facebook @realjonfleetwood
FDA Documents
The code also appears on FDA documents related to Pfizer’s COVID shot.
One FDA document, dated August 23, 2021, regarding the Biologics License Application (BLA) approval for Pfizer-BioNTech Manufacturing GmbH’s COVID-19 Vaccine, mRNA, also features the (b) (4) weapons code.
The license authorized BioNTech to manufacture and distribute the COVID shots.
The document details manufacturing locations, labeling requirements, and postmarketing commitments, including studies focused on vaccine safety and efficacy, as well as monitoring for adverse effects such as myocarditis and pericarditis.
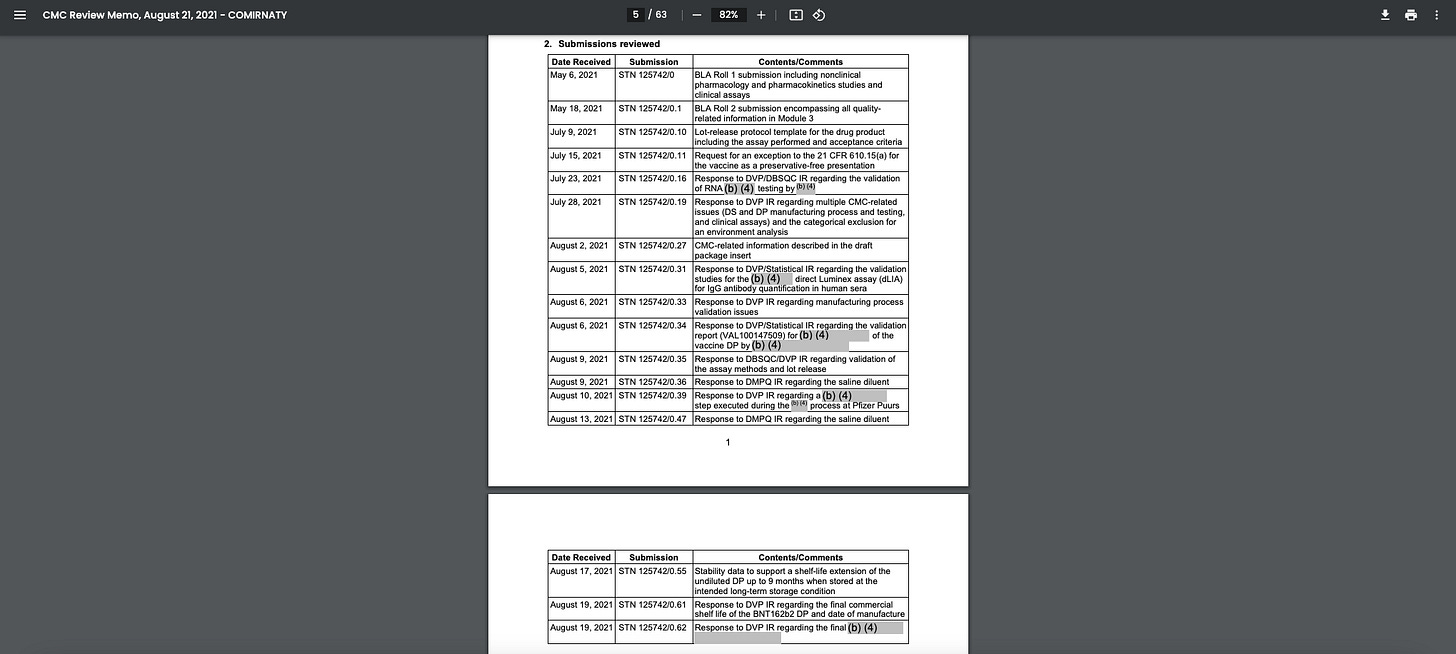
Another FDA document, a CMC (Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Control) Review Memo for Pfizer’s COVID jab, dated August 21, 2021, contains detailed information about the manufacturing process, quality control, and other regulatory aspects of the injection.
The document includes redacted sections displaying the (b) (4) weapons code.

Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood / Facebook @realjonfleetwood
Redacted Data Tied to U.S. Weapon Systems Sparks Fears of a Hidden Bioweapons Agenda
The revelation that sections of Pfizer’s mRNA COVID-19 shot safety data were redacted under a code typically used to protect U.S. weapon systems raises profound concerns about the intersection of public health and national security.
This issue echoes the broader historical context of the United States’ engagement with biological weapons, as detailed in this website’s past investigative reporting.
Historically, the U.S. has been involved in extensive biological weapons programs, dating back to World War II and continuing through the Cold War.
These programs weaponized a variety of pathogens, including anthrax and botulinum toxin, and conducted field tests on unsuspecting civilians and military personnel.
The legacy of these programs has left a complicated and often controversial footprint on both public health and national security.
Fast forward to today, the redactions in Pfizer’s documents invoke similar concerns.
The use of a declassification exemption code typically reserved for state-of-the-art technology within U.S. weapon systems suggests that the technologies or methodologies involved in the vaccine’s development might have dual-use potential—serving both civilian health purposes and military applications.
This dual-use nature raises ethical questions about transparency, especially in light of the historical secrecy surrounding bioweapons development.
This website’s past reporting also highlights how governments, under the guise of “peaceful” or “protective” purposes, can develop technologies that straddle the line between public health and bioweapons.
The Biological Weapons Convention (BWC), while prohibiting the development of bioweapons for hostile purposes, allows for the creation of biological agents for prophylactic or defensive uses, such as vaccines.
This loophole has led to widespread concern about the potential for conflicts of interest, where the same entities that develop vaccines also have a vested interest in the continued existence of the threats those vaccines are meant to counteract.
The implications are stark: if technologies used in vaccine development are also relevant to U.S. defense, it could suggest that the COVID-19 vaccine’s creation was not solely a public health endeavor but potentially intertwined with national security strategies.
This intertwining raises questions about the motivations behind certain aspects of the vaccine’s development and the extent to which public health priorities were balanced with or subordinated to defense interests.
At a time when public trust in health authorities is already strained, these redactions—coupled with the historical precedent of bioweapons programs—invite speculation about the broader purposes behind vaccine development.
Is the public being fully informed about the technologies and methodologies at play, or are critical aspects being withheld under the veil of national security?
This tension between transparency and security mirrors the broader historical narrative of bioweapons, where public safety has often been weighed against the imperatives of national defense, sometimes with questionable results.
This website’s reporting on past and potential future pandemics underscores the need for vigilance in understanding the full scope of government activities related to bioweapons and public health.
The parallels between historical bioweapons programs and the current redactions in vaccine data suggest that the lessons of the past remain relevant today.
As public discourse continues to evolve around these issues, it is crucial to ensure that transparency and accountability are maintained, particularly when the stakes involve both public health and national security.
Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood / Facebook @realjonfleetwood
American Bioweapons: Then & Now
The United States had an extensive offensive biological weapons program stretching back at least to World War II and the Cold War era.
Treaty 'Loophole' Allows World Governments to Develop Deadly Bioweapons Like COVID and Corresponding Vaccines: Yale Professor (Video)
The ‘Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and On Their Destruction,’ known as the “Biological Weapons Convention” (BWC), was opened for signature in April 1972 and took effect in March 1975.
PCR Test Now Being Used to Detect Bird Flu Is 97% Unreliable: Oxford Academic Journal 'Clinical Infectious Diseases'
A September 2020 publication in Clinical Infectious Diseases confirms that the test method known as ‘reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction’ (RT-PCR), currently being used to detect the presence of the bird flu virus, is accurate less than 3% of the time.
FDA to Skip Drug Approval Process for Bird Flu Vaccine: Dr. Peter Marks Confirms Agency Will Leverage Controversial 'Emergency Use Authorization' (EUA) Tactic as It Did with Deadly COVID Jab
Dr. Peter Marks, Director of the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), confirmed last week that the FDA will skip the rigorous drug approval process for influenza bird flu (H5N1) vaccines, as it did for COVID-19 jabs.
U.S. Gov't Is Making a Vaccine for a Virus It Also Happens to Be Making More Deadly: Bird Flu
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) is spending $1 million of American taxpayer money to fund gain-of-function experiments on dangerous bird flu (avian influenza) viruses in collaboration with Chinese scientists, according to a new report.
USDA Developed mRNA Bird Flu Vaccine Against 2.3.4.4b H5N1 As It Made That Virus More Infectious and Deadly with Gain-of-Function—Now the Same Virus Subtype Is Causing the Next Pandemic
A Thursday publication in the peer-reviewed journal Nature confirms the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has been developing an mRNA vaccine for the very same influenza virus, subtype, and clade that is reportedly causing the coming bird flu pandemic: 2.3.4.4b H5N1.
Will the Supreme Court Save Us from Bird Flu Pandemic Tyranny?
Four recent decisions from the U.S. Supreme Court may rein in the government’s enforcement and creation of regulations in response to the apparently incoming bird flu pandemic.
Bird Flu: CPT Code Update Readies U.S. Health Systems for New mRNA Jab Rollout Skipping FDA Approval Process
In anticipation of a coming avian influenza (bird flu) pandemic, the American Medical Association (AMA) on Friday announced an editorial update to the ‘Current Procedural Terminology’ (CPT) code set in order to account for the development and administration of bird flu “vaccines.”
Major Bird Flu Summit October 2-4 in Washington D.C.—Evidence of an Orchestrated Pandemic?
The United States government has been enhancing the transmissibility and lethality of the H5N1 influenza bird flu virus through gain-of-function (GOF) experimentation for years.
U.S. Gov't Manufactures Bird Flu PCR Test In-House Without Third-Party Oversight
The United States government has come under scrutiny for manufacturing the bird flu PCR test in-house without third-party oversight, raising concerns about the accuracy and reliability of the tests as well as their purpose.
New H5N1 Bird Flu Strain May Have Come from U.S. Biolab: McCullough Study Corroborates Earlier JonFleetwood.com Reports
A recent preprint paper authored by Nicolas Hulscher, John Leake, and Dr. Peter McCullough proposes that…
U.S. Gov't Taps Pfizer, Moderna for mRNA Bird Flu Jabs Despite Already-Available Safe, Effective Treatments
The U.S. government is nearing an agreement to bankroll a late-stage trial of Moderna Inc.’s mRNA bird flu vaccine (mRNA-1038), Financial Times reports.

































Cacotopia