Death Reported in Unvaccinated Individuals Infected by Those Vaccinated for Monkeypox: FDA Package Insert
Mpox vaccine ACAM2000 contains live virus that can "shed and be transmitted to close contacts," according to the manufacturer, raising informed consent issues.
The monkeypox vaccine ACAM2000 contains a live virus that the vaccinated can spread to and even kill those who have not received the jab, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood / Facebook @realjonfleetwood
The revelation comes as the World Health Organization (WHO) reports nearly 30 suspected monkeypox cases in Africa since early 2024.
ACAM2000 is manufactured by Emergent BioSolutions Inc., an American multinational specialty biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Gaithersburg, Maryland.
The largest shareholders of Emergent BioSolutions are BlackRock and Vanguard.

The biopharmaceutical company received FDA approval last month for its supplemental biologics license application for ACAM2000 (Smallpox and Mpox (Vaccinia) Vaccine, Live), expanding its use to include the prevention of Mpox.
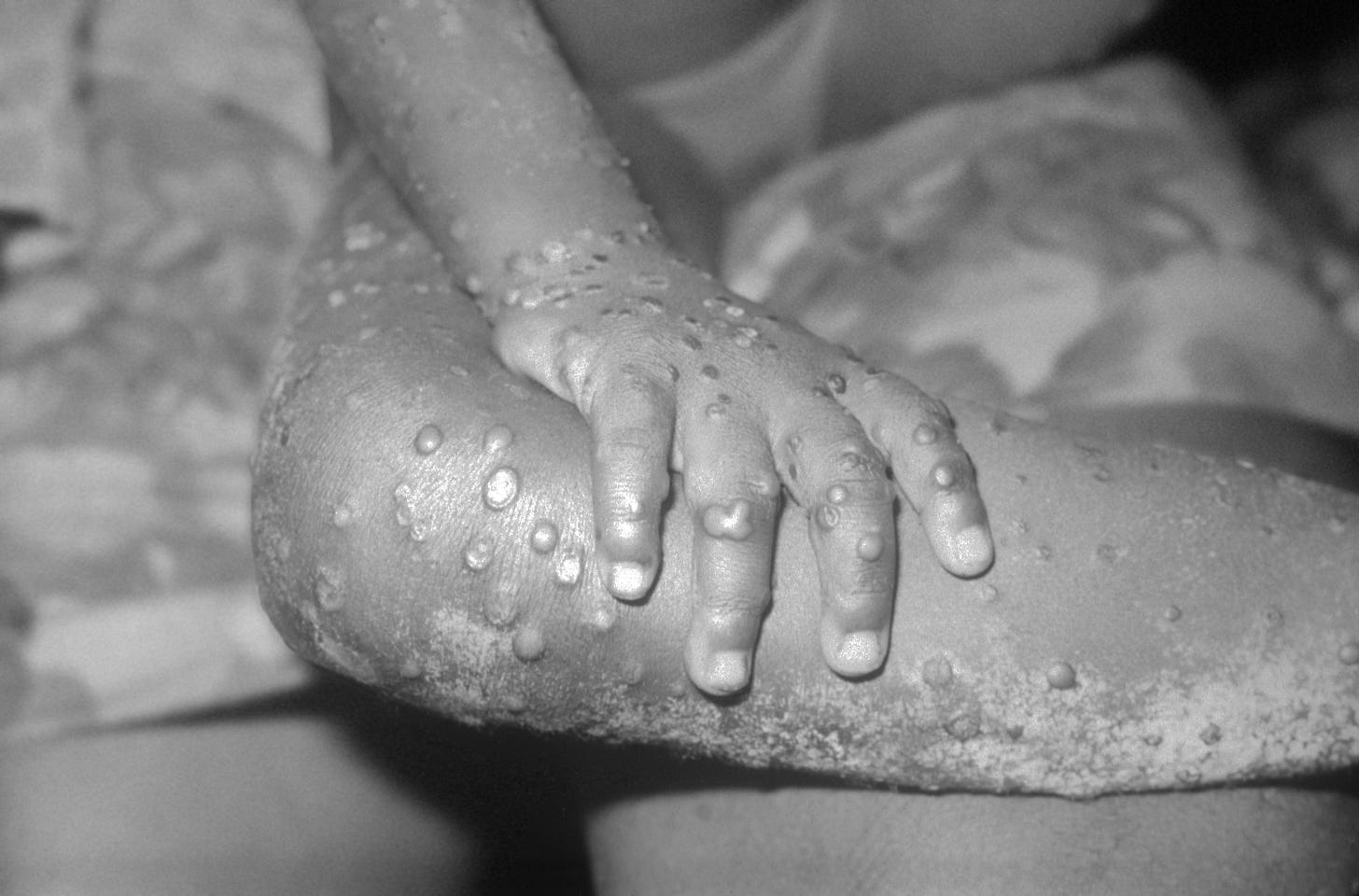
Ironically, ACAM2000 can cause side effects like vesiculopustular eruptions, papules, and pustules, which resemble the skin symptoms seen in monkeypox infections.
These involve pustules, papulovesicular rashes, and lesions on various parts of the body.
Monkeypox itself typically presents with a similar progression of skin lesions, including papules, vesicles, pustules, and scabs.
This website was the first to report that China’s Wuhan laboratory engineered monkeypox DNA fragments after Dr. Anthony Fauci’s NIAID (National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases) authorized funding for mpox gain-of-function experiments, raising lab leak worries.
Shedding
The FDA insert for ACAM indicates the vaccinated can spread the live virus to the unvaccinated, an act known as ‘shedding.’
The document says that “live vaccinia virus can shed and be transmitted to these close contacts.”
“Virus is shed from the vaccination site during the period starting with the development of a papule (day 2-5); shedding ceases when the scab separates and the lesion is re-epithelialized, typically 3-6 weeks after vaccination,” the insert adds. “Steps should be taken in clinical use to reduce the risk of accidental infection of other sites in the vaccinated patient or of contact spread to other individuals.”
The vaccine can cause “accidental inoculation of household members or other close contacts.”
This raises significant informed consent issues, as unvaccinated individuals are exposed to the live virus without their knowledge or consent.
Since the vaccinated can unintentionally spread the virus to close contacts, those at risk of exposure aren’t given the opportunity to make an informed decision about potential infection.
Death in Unvaccinated
The FDA insert for ACAM2000 confirms a risk of death for unvaccinated individuals who come into contact with those vaccinated.
“Death has also been reported in unvaccinated contacts accidentally infected by individuals who have been vaccinated,” the insert reads.
Risk to Expecting Mothers
The risk to pregnant women is unknown because ACAM2000 “has not been studied in pregnant women,” according to the FDA insert.
“Based on data from historical use of other live vaccinia virus vaccines, ACAM2000 can cause fetal vaccinia and fetal death,” the document says.
“If ACAM2000 is administered during pregnancy or within 6 weeks before becoming pregnant, the vaccinee should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Vaccinees should be counseled to avoid becoming pregnant (or getting their partner pregnant) for 6 weeks after vaccination and until the vaccination site has healed.”
Moreover, unvaccinated pregnant women somehow need to be aware of the vaccination status of those around them because vaccinated individuals can shed the virus onto the expecting mother, causing “adverse fetal outcomes.”
“Pregnant women who are close contacts of vaccinees may be at risk of adverse fetal outcomes because ACAM2000 live vaccinia virus can be transmitted from vaccines,” the insert says.
ACAM2000 has also “not been studied in lactating women.”
“It is not known whether ACAM2000 is excreted in human milk,” per the document. “No human or animal data are available to assess the effects of ACAM2000 on the breastfed infant or on milk production/excretion.”
This again highlights a critical informed consent issue, as pregnant or breastfeeding women may unknowingly be exposed to the live virus through vaccinated individuals, putting both themselves and their unborn or breastfeeding children at risk without their consent or adequate information on potential dangers.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The FDA insert for ACAM2000 says that the vaccine has not been tested to see if it could cause cancer, genetic mutations, or affect the ability of men or women to have children.
The drug “has not been evaluated for carcinogenic or mutagenic potential, or for impairment of male or female fertility in animals,” it reads.
You can download the full FDA insert for ACAM2000 below:
Follow Jon Fleetwood: Instagram @realjonfleetwood / Twitter @JonMFleetwood / Facebook @realjonfleetwood
China's Wuhan Lab Engineered Monkeypox DNA Fragments After Fauci's NIAID Funded Monkeypox Gain-of-Function Experiments
In June 2015, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) approved gain-of-function (GOF) experiments that would make monkeypox viruses more infectious and deadly.
Japan to Roll Out New Self-Replicating samRNA COVID Shot That Produces Even More Toxic Spike Protein in the Body Than Regular mRNA Jabs
Meiji Seika Pharma announced plans on Tuesday to seek approval in Japan for its self-amplifying mRNA (samRNA) COVID-19 vaccine, Kostaive (ARCT-2301), with a goal of distributing it for the upcoming fall and winter seasons.
After U.S. Military 'Genetically Engineers' Plague DNA Into E. Coli Bacteria, WHO Adds Black Death to New Pandemic Watchlist, Raising 'Bioweapon' Concerns: Journal 'Access Microbiology'
The Black Death plague, bird flu, and monkeypox are among 24 threats that have been added to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) watchlist of the pathogens “that could trigger the next pandemic,” The Telegraph first reported on Tuesday.
Ebola Vaccine That 'Sheds' in 31% of Vaccinated Given to Colorado Healthcare Workers Just Down the Road from New Bat Lab
Editor’s note: This article’s headline has been updated to clarify that the FDA insert for Merck’s ERVEBO Ebola vaccine states that the vaccine “sheds” in more than 31% of those vaccinated with the drug. The prior headline said that the vaccine “‘Sheds’ Onto/Infects Others 31% of the Time.” It is more precise to simply say that the vaccine “sheds” in 31…
COVID Vaccinated Could Shed Lipid Nanoparticles, Spike Protein Through Blood Transfusion, Breastmilk, Organ Transplantation, Exhalation, Skin-to-Skin Contact: New Preprint Study
A new study made available online today in preprint analyzes exposure to COVID-19 vaccine components such as lipid nanoparticles or spike protein.
Rising Worldwide Cases of Measles, Which Pfizer's Safety Data Links to COVID-19 Vaccine
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and mainstream news are reporting an increase in measles cases around the United States.
FDA-Approved Drugs Nitazoxanide (NTZ) and Monoclonal Antibodies 'Inhibit' Ebola
Healthcare workers at Denver Health in Colorado were recently injected with a “live” Ebola vaccine that has a 31% “shed” rate, according to the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) insert.
U.S. Measles Outbreaks Follow MMR Vaccination Campaign
America might be “on the precipice of a major measles outbreak,” according to mainstream news reports.










It's amazing to me that the USDA included the risk of death in their insert. Amiodarone is a drug used for heart issues. One of its side effects is listed as death. The doctors are fairly cavalier about prescribing it. Oh, the stories I could tell.
Okay, so we're all supposed to run out and get the moneypox jab or it'll kill us anyway?